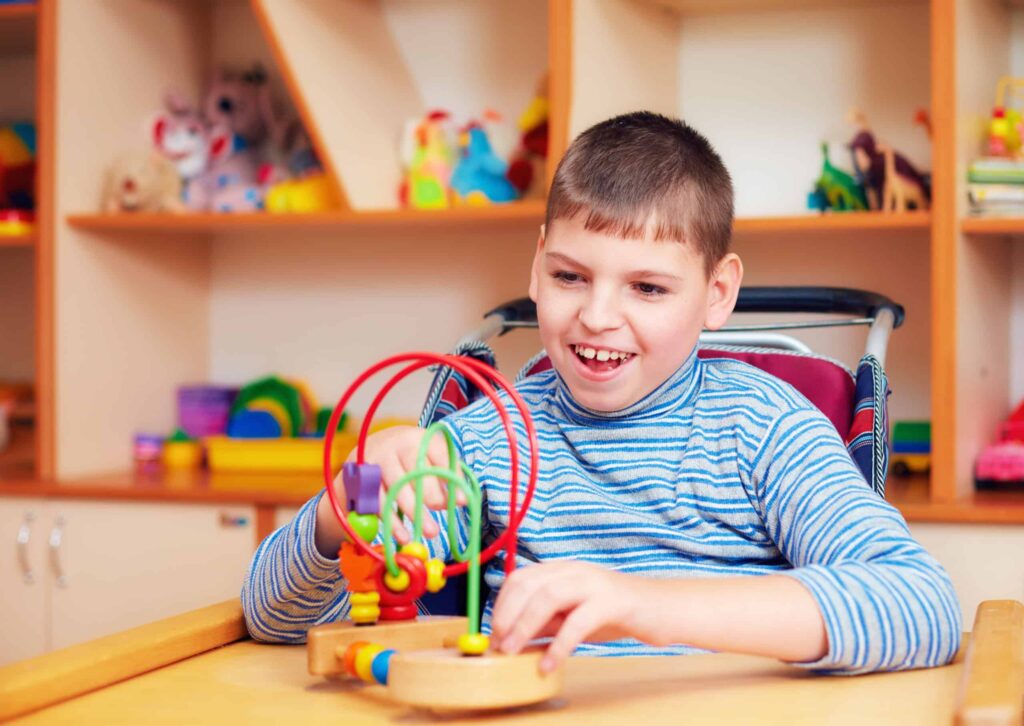
Developing new drugs is a rigorous and detailed process, requiring close scrutiny and testing across clinical trials in order for the drug to successfully find its way to market.
The development process is necessary for understanding drug safety and efficacy before it becomes available for public use. And with patients at the heart of clinical trials, it is vital for researchers to engage with participants in a way that not only carries out research on patients, but with patients.
Patient engagement in clinical trials involves participants from the very beginning of the research process, intended to improve the overall study design and deliver clearer outcomes. A strong level of patient engagement also provides a stronger understanding of patients’ needs throughout the clinical development journey.
This benefits clinical trials by encouraging better patient retention, satisfaction and motivation amongst both patients and researchers.
There are many opportunities to improve patient engagement in clinical trials, from increasing public awareness and improving trial access, to integrating patient needs within a specialised trial design.
Why is patient engagement important in clinical trials?
Patient engagement is one of the most important aspects of clinical research, and is not to be underestimated in its ability to improve the trial’s success.
When developing new drugs or treatments, patients are at the very centre of the process, and clinical trials cannot happen without them. It is important that patient data is recorded thoroughly during the study process in order to understand the complexities of conditions and their treatments.
This requires effective patient engagement and communication from experts across multiple disciplines, all of whom should share a good level of involvement with patients.
Without effective patient engagement, experts cannot collect patient data as accurately and extensively, especially where research involves self-reported side effects from its participants
Patient engagement in clinical trials is not only important for understanding how patients respond to treatment, but also reassuring patients with clear research motives and expectations – which when neglected, have been found to hamper patient involvement.
Patient engagement in rare disease clinical trials
For more common conditions, clinical trials are supported with a huge amount of data from patient groups. And although involvement from patients is important here, it is especially important for researchers to effectively engage with patients in rare disease trials.
For rare conditions, clinical trials face the challenge of patients being harder to find. And with so much more to learn about rare diseases, effective engagement is especially important for fully understanding patient needs.
Patients with rare diseases often suffer from debilitating conditions and are located all across the world. Many may also have limited travelling ability due to their affliction.
These challenges make it vital for clinical trial designs to incorporate a strong patient engagement approach, reducing the likelihood of patient drop-out and standing the best chance of developing rare disease treatments.
Read more: Engaging With Patients And Experts To Develop New Drugs, Page 17
Raising Public Awareness of Clinical Trials
There are several considerations to make when improving patient engagement in clinical trials. During the early stages, it’s important to firstly consider patient enrollment.
Without effective public awareness of the clinical trial, eligible patients and volunteer populations may not realise the research is taking place, despite being willing to potentially get involved.
It is therefore vital to engage with target populations during the enrollment stage of clinical research. Key ways to raise awareness can include:
- Sharing trial information with relevant healthcare bodies and reputable media outlets. Ensure that information is clear, specific and transparent, helping external parties share information accurately.
- Devising a clear communication strategy. It is helpful to provide as much material as possible, answering any potential questions that participants may have and directly address their needs. This should also outline the study’s objectives and provide a clear idea of what the process involves.
- Using advertisements. This can help easily raise awareness of clinical trials amongst target groups and provide a simple way to find out more information about the trial.
Raising awareness through these methods helps improve chances of reaching patient groups. Especially where healthcare practitioners can inform patients of clinical trials they may be eligible for, and can even offer the trial as a treatment option.
When devising communications materials, the public perception of clinical research should be well considered. It is important to emphasise the mutually beneficial nature of research, encouraging a favourable perception of trial processes.
Communicating with patients effectively
Patient engagement is fundamentally led by communication. Not only between the research organisation and wider patient populations, but between the researcher and patient themselves.
Effective and clear communication with patients is essential for reducing any confusion around trial protocols and processes. This may involve:
- Presenting information in a way that’s suitable for the patient. For instance, we created comic book style information packs to help patient engagement amongst younger participants.
- Repeating information clearly, ensuring that patients have understood information thoroughly and important aspects have not been missed
- Avoiding industry terms, using simple, everyday language to describe clinical processes and procedures. A good way to do this is by comparing processes to everyday events that patients might be more familiar with.
- Check the patient has understood the information correctly, prompting feedback from participants to make sure their interpretation is correct.
When patients understand exactly what is expected from them throughout the clinical trial process, as well as what to expect from researchers, they are much less likely to drop out of the study.
Researchers should therefore be well-informed about the entire trial process, helping manage patient expectations and clearly outlining the next steps. Information should be delivered in simple, easy-to-understand terms in order to facilitate better patient engagement.
How does effective communication impact patient engagement?
Using effective communication with patients throughout the clinical development process allows for a more open and honest dialogue, where researchers are able to understand how to make the patient comfortable as well as their experiences.
This can encourage patients to feel more comfortable when disclosing symptoms or responses to treatment, as well as helping them voice any potential concerns.
An open dialogue is especially important in the case of rare disease trials, where there can be fewer assumptions about what the patient may be experiencing and the kind of care they require.
Patient engagement in rare disease clinical trials may therefore involve the researcher communicating with not only the patient, but their families, primary carers and other experts. Especially as 50% of those diagnosed with rare diseases are children, who may require an adult to effectively communicate on their behalf.
Creating patient-centric clinical trial designs
Patient engagement in clinical trials can be significantly improved by involving patients within the trial design.
With a tailored design that recognises patients’ specific requirements, trials can proceed with the right protocols and processes that offer a comfortable experience, ensuring that patients are motivated and engaged. By integrating patient needs within the trial design, participants are much less likely to drop out.
Determining specific needs requires close collaboration between CROs, sponsors, patient advocacy groups and patients. When patient concerns are understood by all parties, trial designers can implement the right methods of support for patients throughout the clinical journey.
The design must allow the research to take place with minimal disruption to the patient’s everyday life. This may involve protocols such as home-based research or support with communication, travel, and other logistical requirements.
Addressing Patient Mental Health
Patient mental health is of the utmost importance. During what can be a timely and heavily involved process, clinical trials may be a lot for patients to deal with. Especially where patients are vulnerable or expressing anxiety around their role in the trial, which is much more common when dealing with rare diseases.
It is vital to open up patient engagement in clinical trials, enabling an open conversation between patients and researchers that allow for an understanding of mental health triggers and how to provide support.
Not only is looking after patient mental health important for the patient themselves, but it is also vital to the trial’s success. For instance, stress related to intrusive clinical assessments and travel are reported as key reasons for patient drop out.
It is therefore important to recognise such triggers and adapt processes in a necessary way that prioritises patient mental health. One way we ensured that the clinical process was as patient-friendly as possible was by organising home based visits where possible, minimising hospital visits – as this can often induce anxiety.
Assessing patients’ experience
In order to understand the effectiveness of patient engagement methods, researchers must make an assessment of patients’ experiences.
This allows researchers to understand how to make trials more patient friendly and improve patient engagement in future clinical trial designs.
Using questionnaires, interviews, patient diaries or other data collection methods, researchers are able to measure the level of patient engagement during the trial process, identifying patient engagement methods that were successful, as well as processes that were not successful.
Summary
By fully understanding the needs of patients, and addressing the trial design to reflect these needs, CROs can begin to improve patient engagement in clinical trials.
Improving patient engagement in clinical trials can result in better delivery and patient retention, both of which allow for more successful development of new drugs and treatments.
These benefits are critical to the success of rare disease trials, where outcomes are dependent on the goodwill and dedication of rare disease patients.